Deep research
Code available here; based on work by Together AI.
This example demonstrates how to build an agentic workflow for deep research—a multi-step reasoning system that mirrors how a human researcher explores, analyzes, and synthesizes information from the web.
Deep research refers to the iterative process of thoroughly investigating a topic: identifying relevant sources, evaluating their usefulness, refining the research direction, and ultimately producing a well-structured summary or report. It’s a long-running task that requires the agent to reason over time, adapt its strategy, and chain multiple steps together, making it an ideal fit for an agentic architecture.
In this example, we use:
- Tavily to search for and retrieve high-quality online resources.
- LiteLLM to route LLM calls that perform reasoning, evaluation, and synthesis.
The agent executes a multi-step trajectory:
- Parallel search across multiple queries.
- Evaluation of retrieved results.
- Adaptive iteration: If results are insufficient, it formulates new research queries and repeats the search-evaluate cycle.
- Synthesis: After a fixed number of iterations, it produces a comprehensive research report.
What makes this workflow compelling is its dynamic, evolving nature. The agent isn’t just following a fixed plan; it’s making decisions in context, using multiple prompts and reasoning steps to steer the process.
Flyte is uniquely well-suited for this kind of system. It provides:
- Structured composition of dynamic reasoning steps
- Built-in parallelism for faster search and evaluation
- Traceability and observability into each step and iteration
- Scalability for long-running or compute-intensive workloads
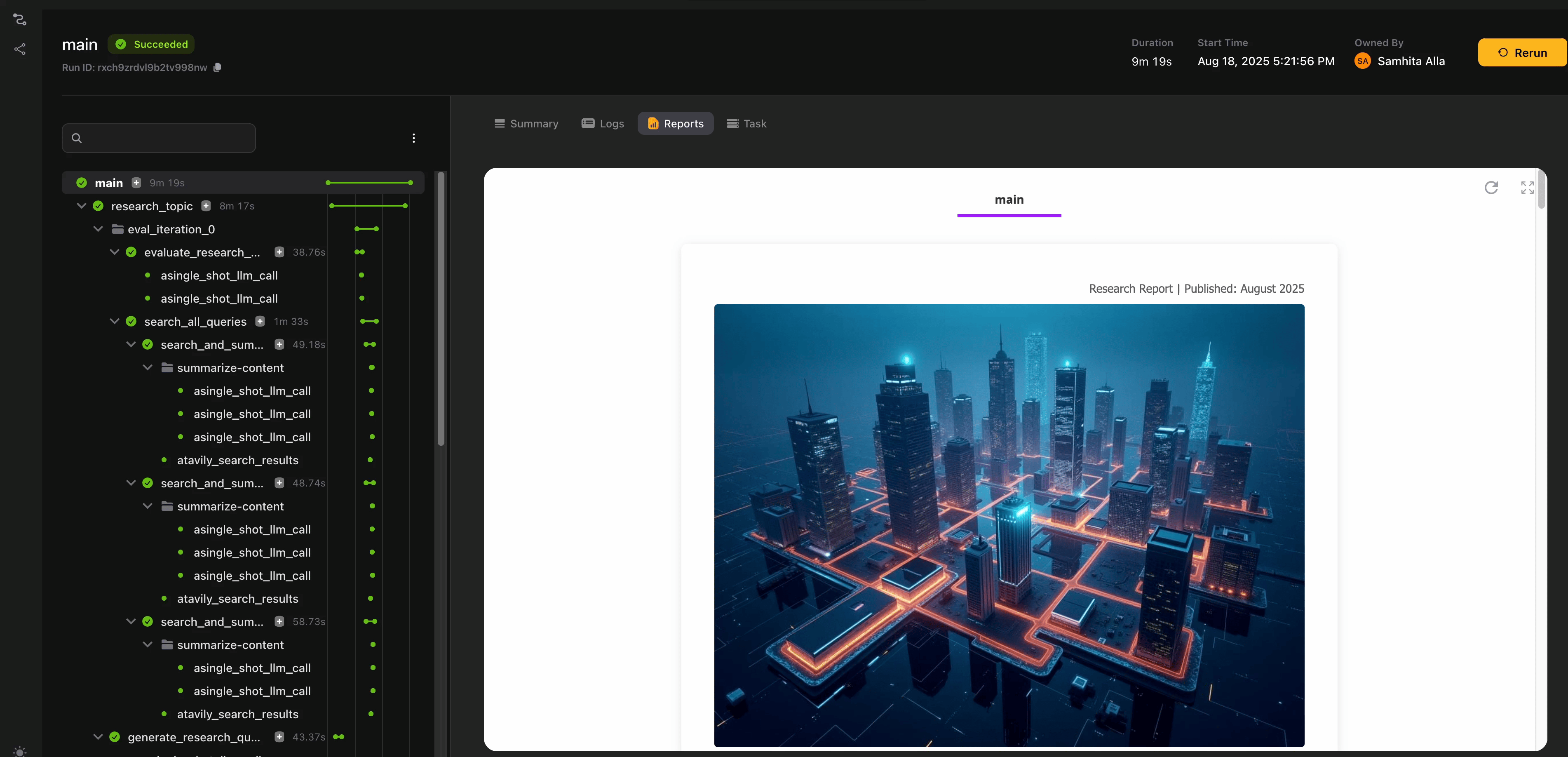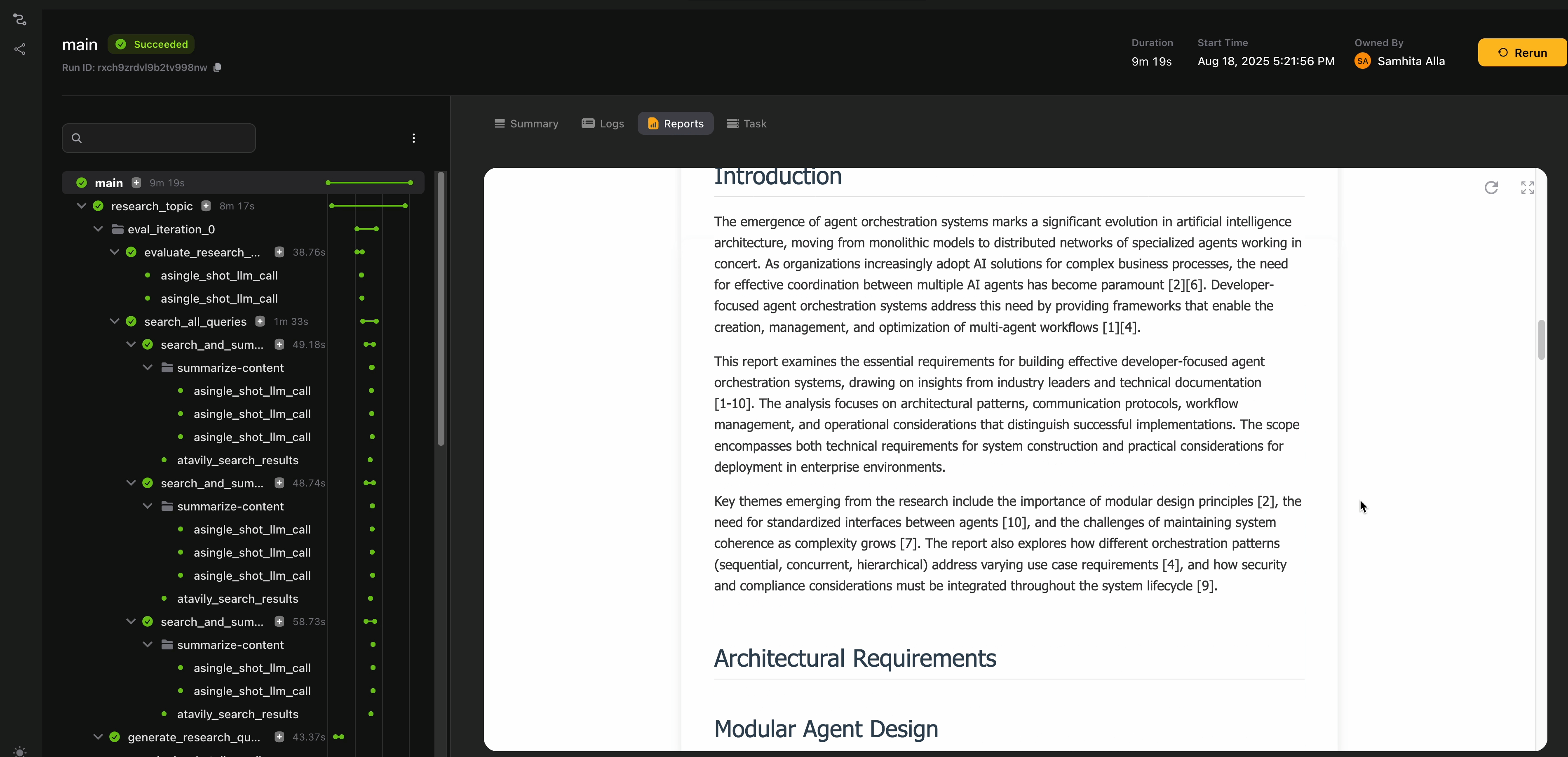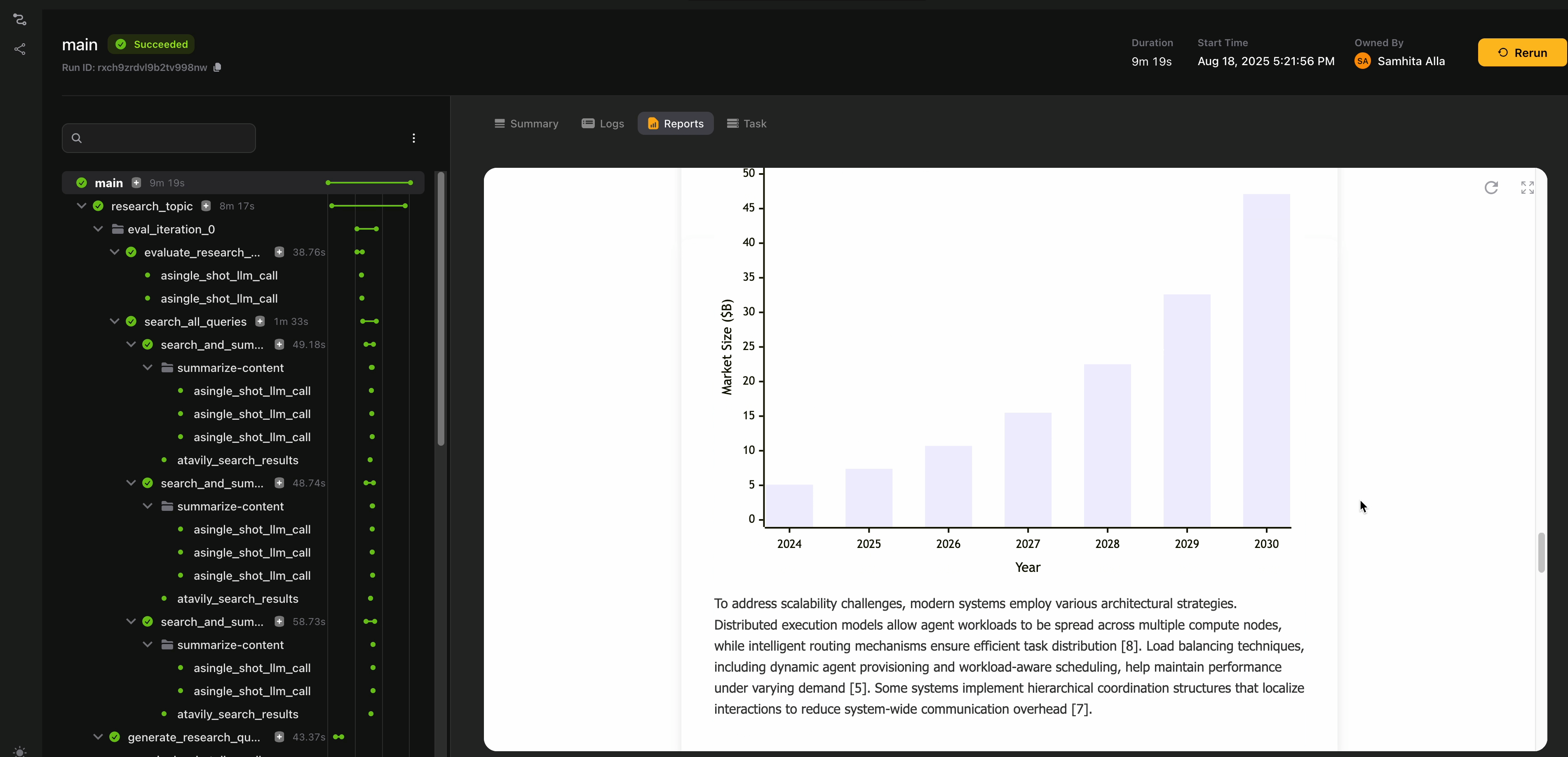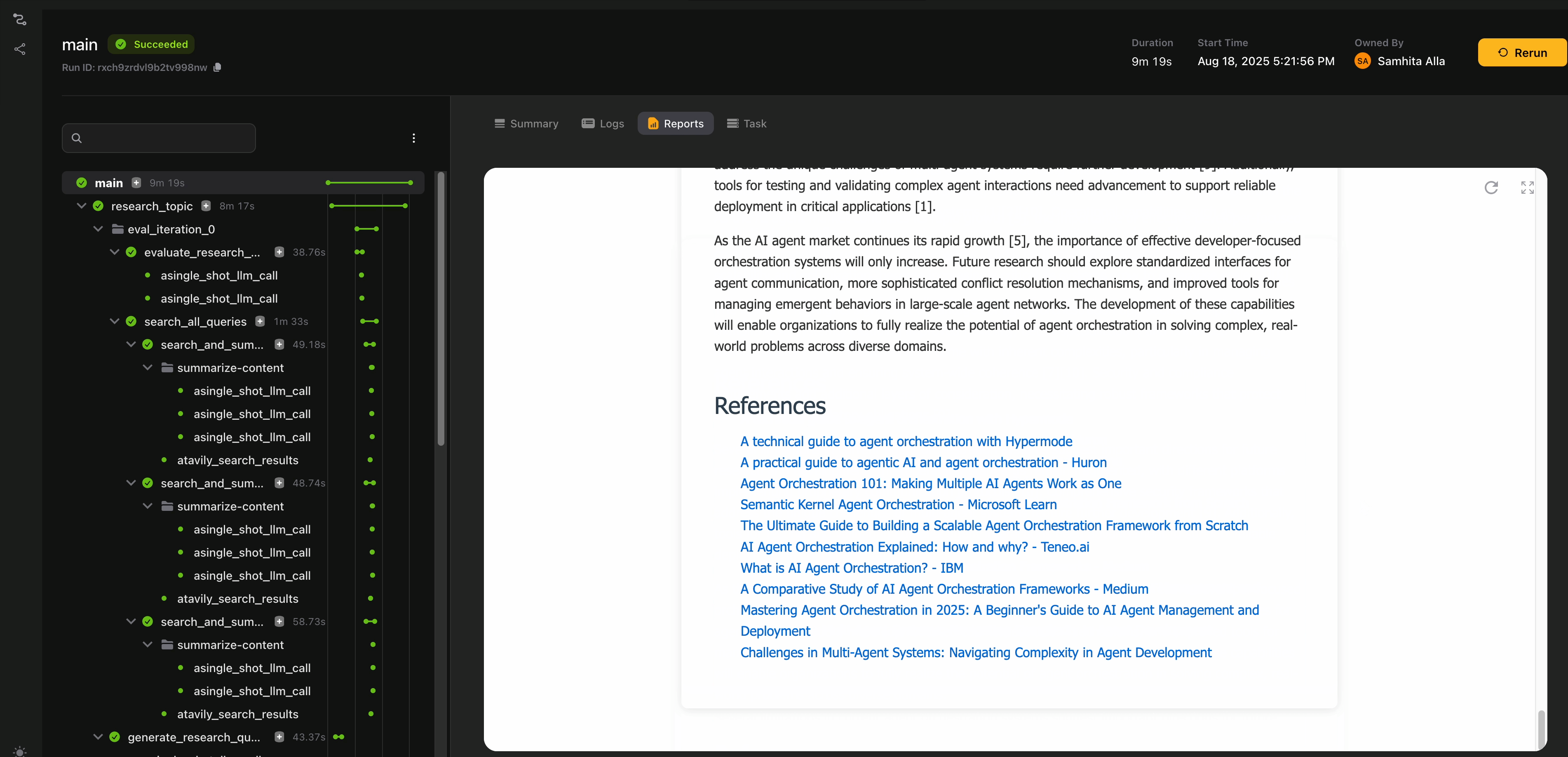
Throughout this guide, we’ll show how to design this workflow using the Flyte SDK, and how to unlock the full potential of agentic development with tools you already know and trust.
Setting up the environment
Let’s begin by setting up the task environment. We define the following components:
- Secrets for Together and Tavily API keys
- A custom image with required Python packages and apt dependencies (
pandoc,texlive-xetex) - External YAML file with all LLM prompts baked into the container
import asyncio
import json
from pathlib import Path
import flyte
import yaml
from flyte.io._file import File
from libs.utils.data_types import (
DeepResearchResult,
DeepResearchResults,
ResearchPlan,
SourceList,
)
from libs.utils.generation import generate_html, generate_toc_image
from libs.utils.llms import asingle_shot_llm_call
from libs.utils.log import AgentLogger
from libs.utils.tavily_search import atavily_search_results
TIME_LIMIT_MULTIPLIER = 5
MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS = 4096
logging = AgentLogger("together.open_deep_research")
env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(
name="deep-researcher",
secrets=[
flyte.Secret(key="together_api_key", as_env_var="TOGETHER_API_KEY"),
flyte.Secret(key="tavily_api_key", as_env_var="TAVILY_API_KEY"),
],
image=flyte.Image.from_uv_script(__file__, name="deep-research-agent", pre=True)
.with_apt_packages("pandoc", "texlive-xetex")
.with_source_file(Path("prompts.yaml"), "/root"),
resources=flyte.Resources(cpu=1),
)
The Python packages are declared at the top of the file using the uv script style:
# /// script
# requires-python = "==3.13"
# dependencies = [
# "flyte>=2.0.0b6",
# "pydantic==2.11.5",
# "litellm==1.72.2",
# "tavily-python==0.7.5",
# "together==1.5.24",
# "markdown==3.8.2",
# "pymdown-extensions==10.16.1",
# ]
# ///Generate research queries
This task converts a user prompt into a list of focused queries. It makes two LLM calls to generate a high-level research plan and parse that plan into atomic search queries.
@env.task
async def generate_research_queries(
topic: str,
planning_model: str,
json_model: str,
prompts_file: File,
) -> list[str]:
async with prompts_file.open() as fh:
data = await fh.read()
yaml_contents = str(data, "utf-8")
prompts = yaml.safe_load(yaml_contents)
PLANNING_PROMPT = prompts["planning_prompt"]
plan = ""
logging.info(f"\n\nGenerated deep research plan for topic: {topic}\n\nPlan:")
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=planning_model,
system_prompt=PLANNING_PROMPT,
message=f"Research Topic: {topic}",
response_format=None,
max_completion_tokens=MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS,
):
plan += chunk
print(chunk, end="", flush=True)
SEARCH_PROMPT = prompts["plan_parsing_prompt"]
response_json = ""
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=json_model,
system_prompt=SEARCH_PROMPT,
message=f"Plan to be parsed: {plan}",
response_format={
"type": "json_object",
"schema": ResearchPlan.model_json_schema(),
},
max_completion_tokens=MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS,
):
response_json += chunk
plan = json.loads(response_json)
return plan["queries"]
LLM calls use LiteLLM, and each is wrapped with flyte.trace for observability:
@flyte.trace
async def asingle_shot_llm_call(
model: str,
system_prompt: str,
message: str,
response_format: Optional[dict[str, str | dict[str, Any]]] = None,
max_completion_tokens: int | None = None,
) -> AsyncIterator[str]:
stream = await acompletion(
model=model,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": message},
],
temperature=0.0,
response_format=response_format,
# NOTE: max_token is deprecated per OpenAI API docs, use max_completion_tokens instead if possible
# NOTE: max_completion_tokens is not currently supported by Together AI, so we use max_tokens instead
max_tokens=max_completion_tokens,
timeout=600,
stream=True,
)
async for chunk in stream:
content = chunk.choices[0].delta.get("content", "")
if content:
yield content
We use flyte.trace to track intermediate steps within a task, like LLM calls or specific function executions. This lightweight decorator adds observability with minimal overhead and is especially useful for inspecting reasoning chains during task execution.
Search and summarize
We submit each research query to Tavily and summarize the results using an LLM. We run all summarization tasks with asyncio.gather, which signals to Flyte that these tasks can be distributed across separate compute resources.
@env.task
async def search_and_summarize(
query: str,
prompts_file: File,
summarization_model: str,
) -> DeepResearchResults:
"""Perform search for a single query"""
if len(query) > 400:
# NOTE: we are truncating the query to 400 characters to avoid Tavily Search issues
query = query[:400]
logging.info(f"Truncated query to 400 characters: {query}")
response = await atavily_search_results(query)
logging.info("Tavily Search Called.")
async with prompts_file.open() as fh:
data = await fh.read()
yaml_contents = str(data, "utf-8")
prompts = yaml.safe_load(yaml_contents)
RAW_CONTENT_SUMMARIZER_PROMPT = prompts["raw_content_summarizer_prompt"]
with flyte.group("summarize-content"):
# Create tasks for summarization
summarization_tasks = []
result_info = []
for result in response.results:
if result.raw_content is None:
continue
task = _summarize_content_async(
result.raw_content,
query,
RAW_CONTENT_SUMMARIZER_PROMPT,
summarization_model,
)
summarization_tasks.append(task)
result_info.append(result)
# Use return_exceptions=True to prevent exceptions from propagating
summarized_contents = await asyncio.gather(
*summarization_tasks, return_exceptions=True
)
# Filter out exceptions
summarized_contents = [
result for result in summarized_contents if not isinstance(result, Exception)
]
formatted_results = []
for result, summarized_content in zip(result_info, summarized_contents):
formatted_results.append(
DeepResearchResult(
title=result.title,
link=result.link,
content=result.content,
raw_content=result.raw_content,
filtered_raw_content=summarized_content,
)
)
return DeepResearchResults(results=formatted_results)
Evaluate research completeness
Now we assess whether the gathered research is sufficient. Again, the task uses two LLM calls to evaluate the completeness of the results and propose additional queries if necessary.
@env.task
async def evaluate_research_completeness(
topic: str,
results: DeepResearchResults,
queries: list[str],
prompts_file: File,
planning_model: str,
json_model: str,
) -> list[str]:
"""
Evaluate if the current search results are sufficient or if more research is needed.
Returns an empty list if research is complete, or a list of additional queries if more research is needed.
"""
# Format the search results for the LLM
formatted_results = str(results)
async with prompts_file.open() as fh:
data = await fh.read()
yaml_contents = str(data, "utf-8")
prompts = yaml.safe_load(yaml_contents)
EVALUATION_PROMPT = prompts["evaluation_prompt"]
logging.info("\nEvaluation: ")
evaluation = ""
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=planning_model,
system_prompt=EVALUATION_PROMPT,
message=(
f"<Research Topic>{topic}</Research Topic>\n\n"
f"<Search Queries Used>{queries}</Search Queries Used>\n\n"
f"<Current Search Results>{formatted_results}</Current Search Results>"
),
response_format=None,
max_completion_tokens=None,
):
evaluation += chunk
print(chunk, end="", flush=True)
EVALUATION_PARSING_PROMPT = prompts["evaluation_parsing_prompt"]
response_json = ""
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=json_model,
system_prompt=EVALUATION_PARSING_PROMPT,
message=f"Evaluation to be parsed: {evaluation}",
response_format={
"type": "json_object",
"schema": ResearchPlan.model_json_schema(),
},
max_completion_tokens=MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS,
):
response_json += chunk
evaluation = json.loads(response_json)
return evaluation["queries"]
Filter results
In this step, we evaluate the relevance of search results and rank them. This task returns the most useful sources for the final synthesis.
@env.task
async def filter_results(
topic: str,
results: DeepResearchResults,
prompts_file: File,
planning_model: str,
json_model: str,
max_sources: int,
) -> DeepResearchResults:
"""Filter the search results based on the research plan"""
# Format the search results for the LLM, without the raw content
formatted_results = str(results)
async with prompts_file.open() as fh:
data = await fh.read()
yaml_contents = str(data, "utf-8")
prompts = yaml.safe_load(yaml_contents)
FILTER_PROMPT = prompts["filter_prompt"]
logging.info("\nFilter response: ")
filter_response = ""
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=planning_model,
system_prompt=FILTER_PROMPT,
message=(
f"<Research Topic>{topic}</Research Topic>\n\n"
f"<Current Search Results>{formatted_results}</Current Search Results>"
),
response_format=None,
max_completion_tokens=MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS,
):
filter_response += chunk
print(chunk, end="", flush=True)
logging.info(f"Filter response: {filter_response}")
FILTER_PARSING_PROMPT = prompts["filter_parsing_prompt"]
response_json = ""
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=json_model,
system_prompt=FILTER_PARSING_PROMPT,
message=f"Filter response to be parsed: {filter_response}",
response_format={
"type": "json_object",
"schema": SourceList.model_json_schema(),
},
max_completion_tokens=MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS,
):
response_json += chunk
sources = json.loads(response_json)["sources"]
logging.info(f"Filtered sources: {sources}")
if max_sources != -1:
sources = sources[:max_sources]
# Filter the results based on the source list
filtered_results = [
results.results[i - 1] for i in sources if i - 1 < len(results.results)
]
return DeepResearchResults(results=filtered_results)
Generate the final answer
Finally, we generate a detailed research report by synthesizing the top-ranked results. This is the output returned to the user.
@env.task
async def generate_research_answer(
topic: str,
results: DeepResearchResults,
remove_thinking_tags: bool,
prompts_file: File,
answer_model: str,
) -> str:
"""
Generate a comprehensive answer to the research topic based on the search results.
Returns a detailed response that synthesizes information from all search results.
"""
formatted_results = str(results)
async with prompts_file.open() as fh:
data = await fh.read()
yaml_contents = str(data, "utf-8")
prompts = yaml.safe_load(yaml_contents)
ANSWER_PROMPT = prompts["answer_prompt"]
answer = ""
async for chunk in asingle_shot_llm_call(
model=answer_model,
system_prompt=ANSWER_PROMPT,
message=f"Research Topic: {topic}\n\nSearch Results:\n{formatted_results}",
response_format=None,
# NOTE: This is the max_token parameter for the LLM call on Together AI,
# may need to be changed for other providers
max_completion_tokens=MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS,
):
answer += chunk
# this is just to avoid typing complaints
if answer is None or not isinstance(answer, str):
logging.error("No answer generated")
return "No answer generated"
if remove_thinking_tags:
# Remove content within <think> tags
answer = _remove_thinking_tags(answer)
# Remove markdown code block markers if they exist at the beginning
if answer.lstrip().startswith("```"):
# Find the first line break after the opening backticks
first_linebreak = answer.find("\n", answer.find("```"))
if first_linebreak != -1:
# Remove everything up to and including the first line break
answer = answer[first_linebreak + 1 :]
# Remove closing code block if it exists
if answer.rstrip().endswith("```"):
answer = answer.rstrip()[:-3].rstrip()
return answer.strip()
Orchestration
Next, we define a research_topic task to orchestrate the entire deep research workflow. It runs the core stages in sequence: generating research queries, performing search and summarization, evaluating the completeness of results, and producing the final report.
@env.task(retries=flyte.RetryStrategy(count=3, backoff=10, backoff_factor=2))
async def research_topic(
topic: str,
budget: int = 3,
remove_thinking_tags: bool = True,
max_queries: int = 5,
answer_model: str = "together_ai/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3",
planning_model: str = "together_ai/Qwen/Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct-Turbo",
json_model: str = "together_ai/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-Turbo",
max_sources: int = 40,
summarization_model: str = "together_ai/meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct-Turbo",
prompts_file: File | str = "prompts.yaml",
) -> str:
"""Main method to conduct research on a topic. Will be used for weave evals."""
if isinstance(prompts_file, str):
prompts_file = await File.from_local(prompts_file)
# Step 1: Generate initial queries
queries = await generate_research_queries(
topic=topic,
planning_model=planning_model,
json_model=json_model,
prompts_file=prompts_file,
)
queries = [topic, *queries[: max_queries - 1]]
all_queries = queries.copy()
logging.info(f"Initial queries: {queries}")
if len(queries) == 0:
logging.error("No initial queries generated")
return "No initial queries generated"
# Step 2: Perform initial search
results = await search_all_queries(queries, summarization_model, prompts_file)
logging.info(f"Initial search complete, found {len(results.results)} results")
# Step 3: Conduct iterative research within budget
for iteration in range(budget):
with flyte.group(f"eval_iteration_{iteration}"):
# Evaluate if more research is needed
additional_queries = await evaluate_research_completeness(
topic=topic,
results=results,
queries=all_queries,
prompts_file=prompts_file,
planning_model=planning_model,
json_model=json_model,
)
# Filter out empty strings and check if any queries remain
additional_queries = [q for q in additional_queries if q]
if not additional_queries:
logging.info("No need for additional research")
break
# for debugging purposes we limit the number of queries
additional_queries = additional_queries[:max_queries]
logging.info(f"Additional queries: {additional_queries}")
# Expand research with new queries
new_results = await search_all_queries(
additional_queries, summarization_model, prompts_file
)
logging.info(
f"Follow-up search complete, found {len(new_results.results)} results"
)
results = results + new_results
all_queries.extend(additional_queries)
# Step 4: Generate final answer
logging.info(f"Generating final answer for topic: {topic}")
results = results.dedup()
logging.info(f"Deduplication complete, kept {len(results.results)} results")
filtered_results = await filter_results(
topic=topic,
results=results,
prompts_file=prompts_file,
planning_model=planning_model,
json_model=json_model,
max_sources=max_sources,
)
logging.info(
f"LLM Filtering complete, kept {len(filtered_results.results)} results"
)
# Generate final answer
answer = await generate_research_answer(
topic=topic,
results=filtered_results,
remove_thinking_tags=remove_thinking_tags,
prompts_file=prompts_file,
answer_model=answer_model,
)
return answer
The main task wraps this entire pipeline and adds report generation in HTML format as the final step.
It also serves as the main entry point to the workflow, allowing us to pass in all configuration parameters, including which LLMs to use at each stage.
This flexibility lets us mix and match models for planning, summarization, and final synthesis, helping us optimize for both cost and quality.
@env.task(report=True)
async def main(
topic: str = (
"List the essential requirements for a developer-focused agent orchestration system."
),
prompts_file: File | str = "/root/prompts.yaml",
budget: int = 2,
remove_thinking_tags: bool = True,
max_queries: int = 3,
answer_model: str = "together_ai/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3",
planning_model: str = "together_ai/Qwen/Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct-Turbo",
json_model: str = "together_ai/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-Turbo",
max_sources: int = 10,
summarization_model: str = "together_ai/meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct-Turbo",
) -> str:
if isinstance(prompts_file, str):
prompts_file = await File.from_local(prompts_file)
answer = await research_topic(
topic=topic,
budget=budget,
remove_thinking_tags=remove_thinking_tags,
max_queries=max_queries,
answer_model=answer_model,
planning_model=planning_model,
json_model=json_model,
max_sources=max_sources,
summarization_model=summarization_model,
prompts_file=prompts_file,
)
async with prompts_file.open() as fh:
data = await fh.read()
yaml_contents = str(data, "utf-8")
toc_image_url = await generate_toc_image(
yaml.safe_load(yaml_contents)["data_visualization_prompt"],
planning_model,
topic,
)
html_content = await generate_html(answer, toc_image_url)
await flyte.report.replace.aio(html_content, do_flush=True)
await flyte.report.flush.aio()
return html_content
Run the deep research agent
First, create the required secrets:
flyte create secret TOGETHER_API_KEY <>
flyte create secret TAVILY_API_KEY <>Run the agent:
uv run --prerelease=allow agent.pyIf you want to test it locally first, run the following commands:
brew install pandoc
brew install basictex # restart your terminal after install
export TOGETHER_API_KEY=<>
export TAVILY_API_KEY=<>
uv run --prerelease=allow agent.pyEvaluate with Weights & Biases Weave
We use W&B Weave to evaluate the full agent pipeline and analyze LLM-generated responses. The evaluation runs as a Flyte pipeline and uses an LLM-as-a-judge scorer to measure the quality of LLM-generated responses.
# /// script
# requires-python = "==3.13"
# dependencies = [
# "flyte>=2.0.0b52",
# "weave==0.51.51",
# "datasets==3.6.0",
# "huggingface-hub==0.32.6",
# "litellm==1.72.2",
# "tavily-python==0.7.5",
# ]
# ///
import os
import weave
from agent import research_topic
from datasets import load_dataset
from huggingface_hub import login
from libs.utils.log import AgentLogger
from litellm import completion
import flyte
logging = AgentLogger()
weave.init(project_name="deep-researcher")
env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(name="deep-researcher-eval")
@weave.op
def llm_as_a_judge_scoring(answer: str, output: str, question: str) -> bool:
prompt = f"""
Given the following question and answer, evaluate the answer against the correct answer:
<question>
{question}
</question>
<agent_answer>
{output}
</agent_answer>
<correct_answer>
{answer}
</correct_answer>
Note that the agent answer might be a long text containing a lot of information or it might be a short answer.
You should read the entire text and think if the agent answers the question somewhere
in the text. You should try to be flexible with the answer but careful.
For example, answering with names instead of name and surname is fine.
The important thing is that the answer of the agent either contains the correct answer or is equal to
the correct answer.
<reasoning>
The agent answer is correct because I can read that ....
</reasoning>
<answer>
1
</answer>
Otherwise, return
<reasoning>
The agent answer is incorrect because there is ...
</reasoning>
<answer>
0
</answer>
"""
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an helpful assistant that returns a number between 0 and 1.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
]
answer = (
completion(
model="together_ai/meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct-Turbo",
messages=messages,
max_tokens=1000,
temperature=0.0,
)
.choices[0] # type: ignore
.message["content"] # type: ignore
)
return bool(int(answer.split("<answer>")[1].split("</answer>")[0].strip()))
def authenticate_huggingface():
"""Authenticate with Hugging Face Hub using token from environment variable."""
token = os.getenv("HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN")
if not token:
raise ValueError(
"HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN environment variable not set. "
"Please set it with your token from https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens"
)
try:
login(token=token)
print("Successfully authenticated with Hugging Face Hub")
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to authenticate with Hugging Face Hub: {e!s}")
@env.task
async def load_questions(
dataset_names: list[str] | None = None,
) -> list[dict[str, str]]:
"""
Load questions from the specified Hugging Face dataset configurations.
Args:
dataset_names: List of dataset configurations to load
Options:
"smolagents:simpleqa",
"hotpotqa",
"simpleqa",
"together-search-bench"
If None, all available configurations except hotpotqa will be loaded
Returns:
List of question-answer pairs
"""
if dataset_names is None:
dataset_names = ["smolagents:simpleqa"]
all_questions = []
# Authenticate with Hugging Face Hub (once and for all)
authenticate_huggingface()
for dataset_name in dataset_names:
print(f"Loading dataset: {dataset_name}")
try:
if dataset_name == "together-search-bench":
# Load Together-Search-Bench dataset
dataset_path = "togethercomputer/together-search-bench"
ds = load_dataset(dataset_path)
if "test" in ds:
split_data = ds["test"]
else:
print(f"No 'test' split found in dataset at {dataset_path}")
continue
for i in range(len(split_data)):
item = split_data[i]
question_data = {
"question": item["question"],
"answer": item["answer"],
"dataset": item.get("dataset", "together-search-bench"),
}
all_questions.append(question_data)
print(f"Loaded {len(split_data)} questions from together-search-bench dataset")
continue
elif dataset_name == "hotpotqa":
# Load HotpotQA dataset (using distractor version for validation)
ds = load_dataset("hotpotqa/hotpot_qa", "distractor", trust_remote_code=True)
split_name = "validation"
elif dataset_name == "simpleqa":
ds = load_dataset("basicv8vc/SimpleQA")
split_name = "test"
else:
# Strip "smolagents:" prefix when loading the dataset
actual_dataset = dataset_name.split(":")[-1]
ds = load_dataset("smolagents/benchmark-v1", actual_dataset)
split_name = "test"
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to load dataset {dataset_name}: {e!s}")
continue # Skip this dataset if it fails to load
print(f"Dataset structure for {dataset_name}: {ds}")
print(f"Available splits: {list(ds)}")
split_data = ds[split_name] # type: ignore
for i in range(len(split_data)):
item = split_data[i]
if dataset_name == "hotpotqa":
# we remove questions that are easy or medium (if any) just to reduce the number of questions
if item["level"] != "hard":
continue
question_data = {
"question": item["question"],
"answer": item["answer"],
"dataset": dataset_name,
}
elif dataset_name == "simpleqa":
# Handle SimpleQA dataset format
question_data = {
"question": item["problem"],
"answer": item["answer"],
"dataset": dataset_name,
}
else:
question_data = {
"question": item["question"],
"answer": item["true_answer"],
"dataset": dataset_name,
}
all_questions.append(question_data)
print(f"Loaded {len(all_questions)} questions in total")
return all_questions
@weave.op
async def predict(question: str):
return await research_topic(topic=str(question))
@env.task
async def main(datasets: list[str] = ["together-search-bench"], limit: int | None = 1):
questions = await load_questions(datasets)
if limit is not None:
questions = questions[:limit]
print(f"Limited to {len(questions)} question(s)")
evaluation = weave.Evaluation(dataset=questions, scorers=[llm_as_a_judge_scoring])
await evaluation.evaluate(predict)
if __name__ == "__main__":
flyte.init_from_config()
flyte.with_runcontext(raw_data_path="data").run(main)
You can run this pipeline locally as follows:
export HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN=<> # https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
export WANDB_API_KEY=<> # https://wandb.ai/settings
uv run --prerelease=allow weave_evals.pyThe script will run all tasks in the pipeline and log the evaluation results to Weights & Biases. While you can also evaluate individual tasks, this script focuses on end-to-end evaluation of the end-to-end deep research workflow.