Distributed training
When running distributed training jobs, multiple processes run simultaneously across GPUs. The @wandb_init decorator automatically detects distributed training environments and coordinates W&B logging across processes.
The plugin:
- Auto-detects distributed context from environment variables (set by launchers like
torchrun) - Controls which processes initialize W&B runs based on the
run_modeandrank_scopeparameters - Generates unique run IDs that distinguish between workers and ranks
- Adds links to W&B runs in the Flyte UI
Quick start
Here’s a minimal single-node example that logs metrics from a distributed training task. By default (run_mode="auto", rank_scope="global"), only rank 0 logs to W&B:
import flyte
import torch
import torch.distributed
from flyteplugins.pytorch.task import Elastic
from flyteplugins.wandb import get_wandb_run, wandb_config, wandb_init
image = flyte.Image.from_debian_base(name="torch-wandb").with_pip_packages(
"flyteplugins-wandb", "flyteplugins-pytorch"
)
env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(
name="distributed_env",
image=image,
resources=flyte.Resources(gpu="A100:2"),
plugin_config=Elastic(nproc_per_node=2, nnodes=1),
secrets=flyte.Secret(key="wandb_api_key", as_env_var="WANDB_API_KEY"),
)
@wandb_init
@env.task
def train() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
# Only rank 0 gets a W&B run object; others get None
run = get_wandb_run()
# Simulate training
for step in range(100):
loss = 1.0 / (step + 1)
# Safe to call on all ranks - only rank 0 actually logs
if run:
run.log({"loss": loss, "step": step})
torch.distributed.destroy_process_group()
return loss
if __name__ == "__main__":
flyte.init_from_config()
flyte.with_runcontext(
custom_context=wandb_config(project="my-project", entity="my-team")
).run(train)
A few things to note:
- Use the
Elasticplugin to configure distributed training (number of processes, nodes) - Apply
@wandb_initas the outermost decorator - Check if
runis not None before logging - only the primary rank has a run object inautomode
if run: check is always safe regardless of run mode. In shared and new modes all ranks get a run object, but the check doesn’t hurt and keeps your code portable across modes.
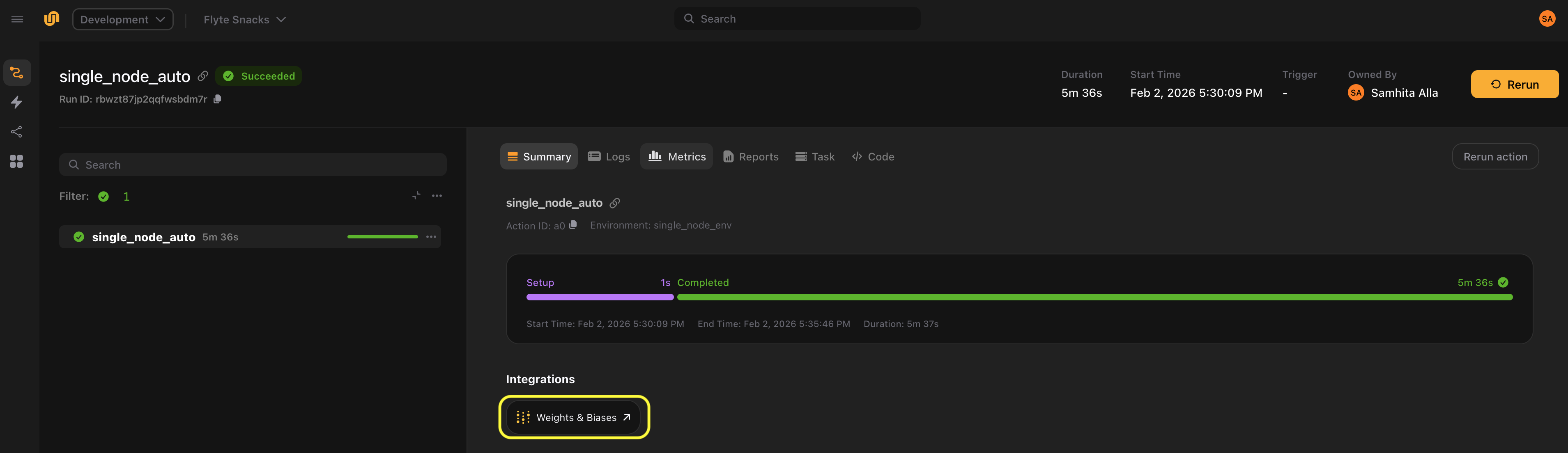
Run modes in distributed training
The run_mode parameter controls how W&B runs are created across distributed processes. The behavior differs between single-node (one machine, multiple GPUs) and multi-node (multiple machines) setups.
Single-node behavior
| Mode | Which ranks log | Result |
|---|---|---|
auto (default) |
Only rank 0 | 1 W&B run |
shared |
All ranks to same run | 1 W&B run with metrics labeled by rank |
new |
Each rank separately | N W&B runs (grouped in UI) |
Multi-node behavior
For multi-node training, the rank_scope parameter controls the granularity of W&B runs:
global(default): Treat all workers as one unitworker: Treat each worker/node independently
The combination of run_mode and rank_scope determines logging behavior:
run_mode |
rank_scope |
Who initializes W&B | W&B Runs | Grouping |
|---|---|---|---|---|
auto |
global |
Global rank 0 only | 1 | - |
auto |
worker |
Local rank 0 per worker | N | - |
shared |
global |
All ranks (shared globally) | 1 | - |
shared |
worker |
All ranks (shared per worker) | N | - |
new |
global |
All ranks | N × M | 1 group |
new |
worker |
All ranks | N × M | N groups |
Where N = number of workers/nodes, M = processes per worker.
Choosing run mode and rank scope
auto(recommended): Use when you want clean dashboards with minimal runs. Most metrics (loss, accuracy) are the same across ranks after gradient synchronization, so logging from one rank is sufficient.shared: Use when you need to compare metrics across ranks in a single view. Each rank’s metrics are labeled with anx_labelidentifier. Useful for debugging load imbalance or per-GPU throughput.new: Use when you need completely separate runs per GPU, for example to track GPU-specific metrics or compare training dynamics across devices.
For multi-node training:
- Use
rank_scope="global"(default) for most cases. A single consolidated run across all nodes is sufficient since metrics like loss and accuracy converge after gradient synchronization. - Use
rank_scope="worker"for debugging and per-node analysis. This is useful when you need to inspect data distribution across nodes, compare predictions from different workers, or track metrics on individual batches outside the main node.
Single-node multi-GPU
For single-node distributed training, configure the Elastic plugin with nnodes=1 and set nproc_per_node to your GPU count.
Basic example with auto mode
import os
import torch
import torch.distributed
import flyte
from flyteplugins.pytorch.task import Elastic
from flyteplugins.wandb import wandb_init, get_wandb_run
env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(
name="single_node_env",
image=image,
resources=flyte.Resources(gpu="A100:4"),
plugin_config=Elastic(nproc_per_node=4, nnodes=1),
secrets=flyte.Secret(key="wandb_api_key", as_env_var="WANDB_API_KEY"),
)
@wandb_init # run_mode="auto" (default)
@env.task
def train_single_node() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", 0))
device = torch.device(f"cuda:{local_rank}")
torch.cuda.set_device(device)
run = get_wandb_run()
# Training loop - only rank 0 logs
for epoch in range(10):
loss = train_epoch(model, dataloader, device)
if run:
run.log({"epoch": epoch, "loss": loss})
torch.distributed.destroy_process_group()
return lossUsing shared mode for per-rank metrics
When you need to see metrics from all GPUs in a single run, use run_mode="shared":
import os
@wandb_init(run_mode="shared")
@env.task
def train_with_per_gpu_metrics() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", 0))
device = torch.device(f"cuda:{local_rank}")
torch.cuda.set_device(device)
# In shared mode, all ranks get a run object
run = get_wandb_run()
for step in range(1000):
loss, throughput = train_step(model, batch, device)
# Each rank logs with automatic x_label identification
if run:
run.log({
"loss": loss,
"throughput_samples_per_sec": throughput,
"gpu_memory_used": torch.cuda.memory_allocated(device),
})
torch.distributed.destroy_process_group()
return loss
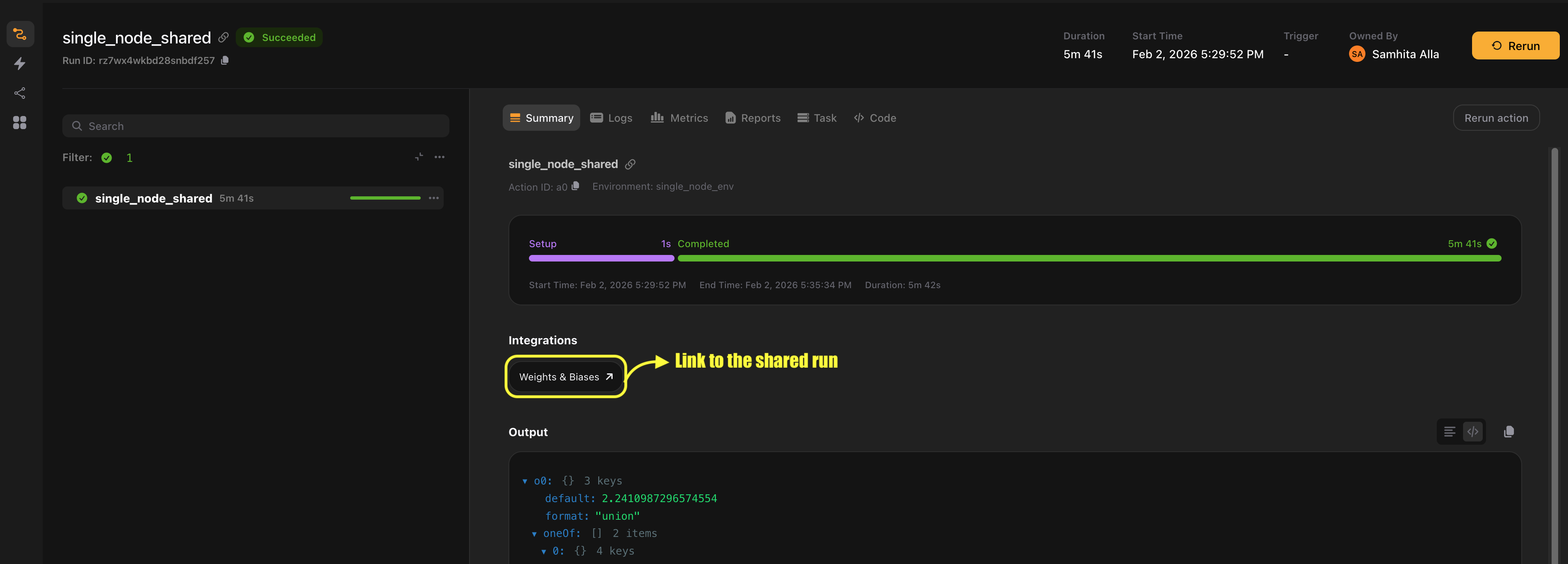
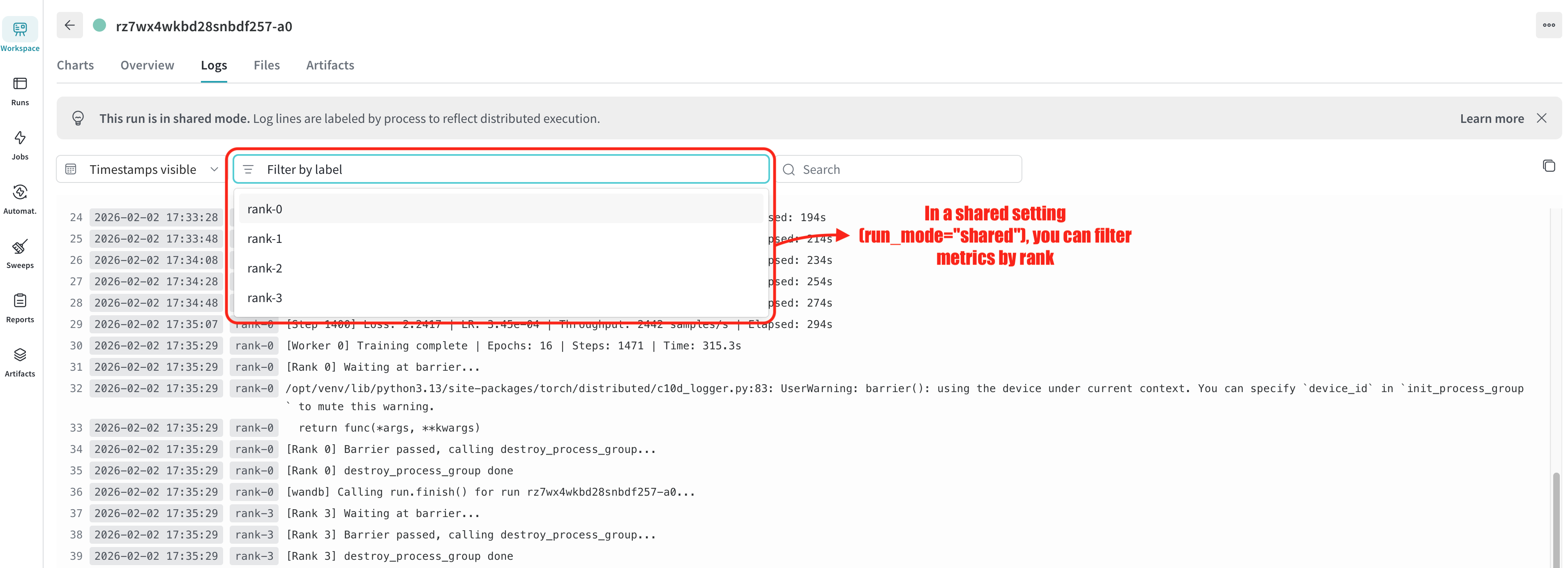
In the W&B UI, metrics from each rank appear with distinct labels, allowing you to compare GPU utilization and throughput across devices.
Using new mode for per-rank runs
When you need completely separate W&B runs for each GPU, use run_mode="new". Each rank gets its own run, and runs are grouped together in the W&B UI:
@wandb_init(run_mode="new") # Each rank gets its own run
@env.task
def train_per_rank() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
# ...
# Each rank has its own W&B run
run = get_wandb_run()
# Run IDs: {base}-rank-{rank}
# All runs are grouped under {base} in W&B UI
run.log({"train/loss": loss.item(), "rank": rank})
# ...With run_mode="new":
- Each rank creates its own W&B run
- Run IDs follow the pattern
{run_name}-{action_name}-rank-{rank} - All runs are grouped together in the W&B UI for comparison
Multi-node training with Elastic
For multi-node distributed training, set nnodes to your node count. The rank_scope parameter controls whether you get a single W&B run across all nodes (global) or one run per node (worker).
Global scope (default): Single run across all nodes
With run_mode="auto" and rank_scope="global" (both defaults), only global rank 0 initializes W&B, resulting in a single run for the entire distributed job:
import os
import torch
import torch.distributed
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, DistributedSampler
import flyte
from flyteplugins.pytorch.task import Elastic
from flyteplugins.wandb import wandb_init, wandb_config, get_wandb_run
image = flyte.Image.from_debian_base(name="torch-wandb").with_pip_packages(
"flyteplugins-wandb", "flyteplugins-pytorch", pre=True
)
multi_node_env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(
name="multi_node_env",
image=image,
resources=flyte.Resources(
cpu=(1, 2),
memory=("1Gi", "10Gi"),
gpu="A100:4",
shm="auto",
),
plugin_config=Elastic(
nproc_per_node=4, # GPUs per node
nnodes=2, # Number of nodes
),
secrets=flyte.Secret(key="wandb_api_key", as_env_var="WANDB_API_KEY"),
)
@wandb_init # rank_scope="global" by default → 1 run total
@multi_node_env.task
def train_multi_node(epochs: int, batch_size: int) -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
world_size = torch.distributed.get_world_size()
local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", 0))
device = torch.device(f"cuda:{local_rank}")
torch.cuda.set_device(device)
# Model with DDP
model = MyModel().to(device)
model = DDP(model, device_ids=[local_rank])
# Distributed data loading
dataset = MyDataset()
sampler = DistributedSampler(dataset, num_replicas=world_size, rank=rank)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, sampler=sampler)
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Only global rank 0 gets a W&B run
run = get_wandb_run()
for epoch in range(epochs):
sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(dataloader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if run and batch_idx % 100 == 0:
run.log({
"train/loss": loss.item(),
"train/epoch": epoch,
"train/batch": batch_idx,
})
if run:
run.log({"train/epoch_complete": epoch})
# Barrier ensures all ranks finish before cleanup
torch.distributed.barrier()
torch.distributed.destroy_process_group()
return loss.item()
if __name__ == "__main__":
flyte.init_from_config()
flyte.with_runcontext(
custom_context=wandb_config(
project="multi-node-training",
tags=["distributed", "multi-node"],
)
).run(train_multi_node, epochs=10, batch_size=32)With this configuration:
- Two nodes run the task, each with 4 GPUs (8 total processes)
- Only global rank 0 creates a W&B run
- Run ID follows the pattern
{run_name}-{action_name} - The Flyte UI shows a single link to the W&B run
Worker scope: One run per node
Use rank_scope="worker" when you want each node to have its own W&B run for per-node analysis:
@wandb_init(rank_scope="worker") # 1 run per worker/node
@multi_node_env.task
def train_per_worker(epochs: int, batch_size: int) -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", 0))
# ...
# Local rank 0 of each worker gets a W&B run
run = get_wandb_run()
if run:
# Each worker logs to its own run
run.log({"train/loss": loss.item()})
# ...With run_mode="auto", rank_scope="worker":
- Each node’s local rank 0 creates a W&B run
- Run IDs follow the pattern
{run_name}-{action_name}-worker-{worker_index} - The Flyte UI shows links to each worker’s W&B run
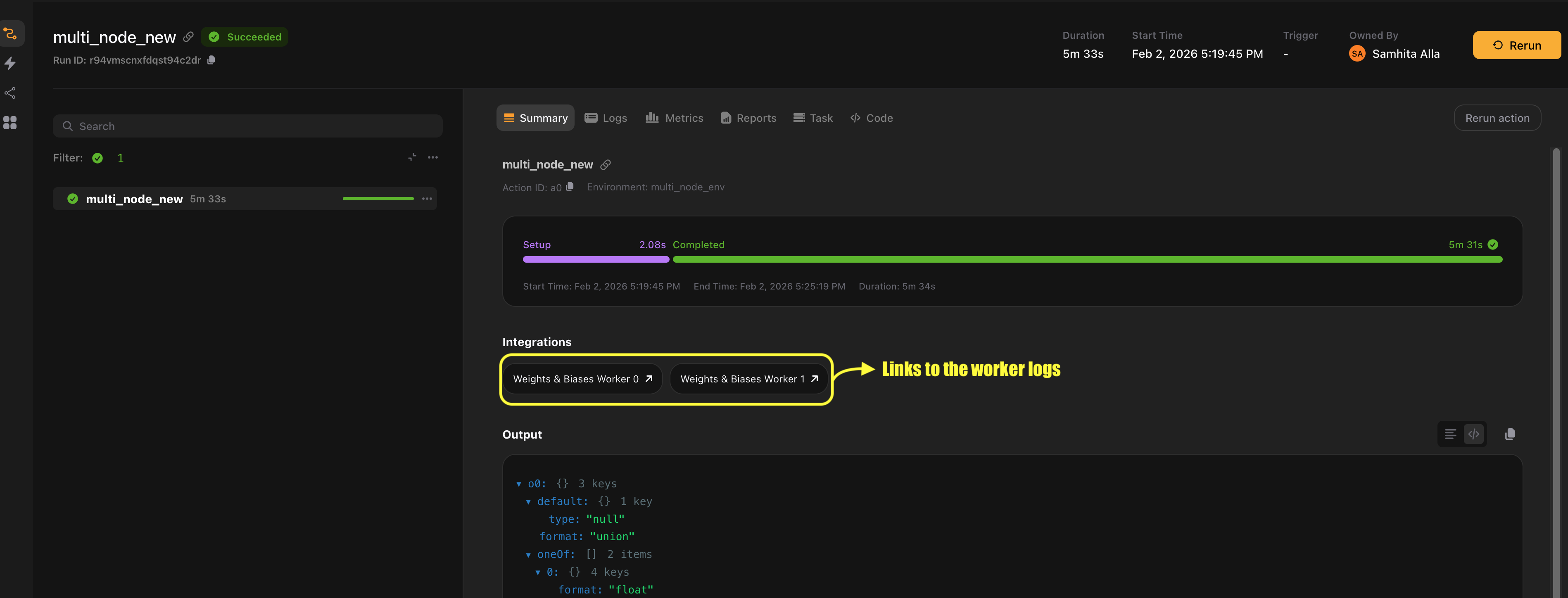
Shared mode: All ranks log to the same run
Use run_mode="shared" when you need metrics from all ranks in a single view. Each rank’s metrics are labeled with an x_label identifier.
Shared + global scope (1 run total)
@wandb_init(run_mode="shared") # All ranks log to 1 shared run
@multi_node_env.task
def train_shared_global() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
# ...
# All ranks get a run object, all log to the same run
run = get_wandb_run()
# Each rank logs with automatic x_label identification
run.log({"train/loss": loss.item(), "rank": rank})
# ...Shared + worker scope (N runs, 1 per node)
@wandb_init(run_mode="shared", rank_scope="worker") # 1 shared run per worker
@multi_node_env.task
def train_shared_worker() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
# ...
# All ranks get a run object, grouped by worker
run = get_wandb_run()
# Ranks on the same worker share a run
run.log({"train/loss": loss.item(), "local_rank": local_rank})
# ...New mode: Separate run per rank
Use run_mode="new" when you need completely separate runs per GPU. Runs are grouped in the W&B UI for easy comparison.
New + global scope (N×M runs, 1 group)
@wandb_init(run_mode="new") # Each rank gets its own run, all in 1 group
@multi_node_env.task
def train_new_global() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
# ...
# Each rank has its own run
run = get_wandb_run()
# Run IDs: {base}-rank-{global_rank}
run.log({"train/loss": loss.item()})
# ...New + worker scope (N×M runs, N groups)
@wandb_init(run_mode="new", rank_scope="worker") # Each rank gets own run, grouped per worker
@multi_node_env.task
def train_new_worker() -> float:
torch.distributed.init_process_group("nccl")
# ...
# Each rank has its own run, grouped by worker
run = get_wandb_run()
# Run IDs: {base}-worker-{idx}-rank-{local_rank}
run.log({"train/loss": loss.item()})
# ...How it works
The plugin automatically detects distributed training by checking environment variables set by distributed launchers like torchrun:
| Environment variable | Description |
|---|---|
RANK |
Global rank across all processes |
WORLD_SIZE |
Total number of processes |
LOCAL_RANK |
Rank within the current node |
LOCAL_WORLD_SIZE |
Number of processes on the current node |
GROUP_RANK |
Node/worker index (0 for first node, 1 for second, etc.) |
When these variables are present, the plugin:
- Determines which ranks should initialize W&B based on
run_modeandrank_scope - Generates unique run IDs that include worker and rank information
- Creates UI links for each W&B run (single link with
rank_scope="global", one per worker withrank_scope="worker")
The plugin automatically adapts to your training setup, eliminating the need for manual distributed configuration.
Run ID patterns
| Scenario | Run ID Pattern | Group |
|---|---|---|
| Single-node auto/shared | {base} |
- |
| Single-node new | {base}-rank-{rank} |
{base} |
| Multi-node auto/shared (global) | {base} |
- |
| Multi-node auto/shared (worker) | {base}-worker-{idx} |
- |
| Multi-node new (global) | {base}-rank-{global_rank} |
{base} |
| Multi-node new (worker) | {base}-worker-{idx}-rank-{local_rank} |
{base}-worker-{idx} |
Where {base} = {run_name}-{action_name}