Add Tracing and Guardrails to an Airbnb RAG App with Weave
This guide shows you how to build a RAG app using Weave, vLLM, and Weaviate, and deploy it on Union.
The app retrieves relevant Airbnb listings based on user queries and generates responses using a self-hosted Phi-3 model. While you can swap in a larger model for production use, this demo uses Phi-3 Mini for its speed and accessibility.
Once you have a Union account, install union:
pip install unionExport the following environment variable to build and push images to your own container registry:
# replace with your registry name
export IMAGE_SPEC_REGISTRY="<your-container-registry>"Then run the following commands to run the workflow:
$ git clone https://github.com/unionai/unionai-examples
$ cd unionai-examples
$ union run --remote <path/to/file.py> <workflow_name> <params>The source code for this example can be found here.
As RAG applications move closer to production, observability and reliability become essential. Without insight into how responses are generated or safeguards to prevent hallucinations and off-topic answers, it’s hard to build trust in your system. This is where Weave comes in:
- 🔍 Trace each step of the RAG pipeline, from user query to generated response.
- 🛡️ Add guardrails to validate and control model outputs.
- 🔧 Debug, evaluate, and iterate on your app with confidence.
While testing the app, we made extensive use of Weave’s tracing to monitor how the model was responding to different queries. This helped us catch and fix issues like hallucinations and off-topic answers early in the development process.
The code is split into two parts:
- Ingestion: Load Airbnb listings into Weaviate with a Union task.
- RAG App:
- Parse user queries to generate metadata filters
- Retrieve relevant listings from Weaviate using those filters
- Generate responses with the self-hosted Phi-3 model
- Add tracing and guardrails with Weave to monitor and validate outputs
With Union, you can run ingestion as a background task while serving user queries in real-time using Union serving. Everything stays in sync and scales — no manual infrastructure management required.
Ingesting Airbnb listings into Weaviate
We start by defining an ingestion task that loads Airbnb listings into Weaviate, a vector database.
import csv
import gzip
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
import union
EMBEDDING_MODEL = "BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5"
image = union.ImageSpec(
name="airbnb-weaviate-ingestion",
packages=[
"llama-index==0.12.32",
"llama-index-vector-stores-weaviate==1.3.1",
"union==0.1.178",
"llama-index-embeddings-fastembed==0.3.1",
],
builder="union",
)
@union.task(
cache=True,
secret_requests=[
union.Secret(key="weaviate-url", env_var="WEAVIATE_URL"),
union.Secret(key="weaviate-api-key", env_var="WEAVIATE_API_KEY"),
],
requests=union.Resources(mem="20Gi", cpu="15"),
container_image=image,
)
def ingest_data(inside_airbnb_listings_url: union.FlyteFile, index_name: str) -> str:
import os
import weaviate
from llama_index.core import Settings, StorageContext, VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.embeddings.fastembed import FastEmbedEmbedding
from llama_index.vector_stores.weaviate import WeaviateVectorStore
from weaviate.classes.init import AdditionalConfig, Auth, Timeout
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud(
cluster_url=os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL"),
auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY")),
additional_config=AdditionalConfig(timeout=Timeout(init=30)),
)
output_file_path = (
Path(union.current_context().working_directory) / "airbnb_listings.csv"
)
with gzip.open(inside_airbnb_listings_url.download(), "rb") as f_in:
with open(output_file_path, "wb") as f_out:
shutil.copyfileobj(f_in, f_out)
documents = []
with open(output_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as fp:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(fp, delimiter=",", quotechar='"')
for row in csv_reader:
documents.append(parse_listing_row(row))
# Set embedding model
Settings.embed_model = FastEmbedEmbedding(model_name=EMBEDDING_MODEL)
# Configure vector store
vector_store = WeaviateVectorStore(weaviate_client=client, index_name=index_name)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
# Index documents
VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, storage_context=storage_context, show_progress=True
)
client.close()
return "Ingestion complete"The task connects to Weaviate using a provided URL and API key (passed as secrets), downloads the dataset from
Inside Airbnb, and processes the listings.
It extracts relevant metadata such as price, review scores, number of reviews, superhost and instant bookable status,
as well as geolocation data like latitude and longitude, which it converts into Weaviate’s GeoCoordinate format.
The task then indexes the processed listings using the VectorStoreIndex class from LlamaIndex.
We enable caching so the task won’t re-run if the data has already been ingested.
Hosting the model
We begin by pulling the model from Hugging Face using the union cache model-from-hf command.
This stores the model as a Union artifact, acting as a cache to reduce network overhead during future deployments.
Next, we define a VLLMApp to deploy the cached model using vLLM.
Make sure to reference the model artifact URI from the previous step in the app’s specification.
import os
import re
import typing
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
import union
import weave
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from flytekit.extras.accelerators import GPUAccelerator
from union.app import App, Input, WeaveConfig
from union.app.llm import VLLMApp
LLM = "microsoft/Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct"
MODEL_ID = "phi-3-mini"
MODEL_ARTIFACT_URI = "<YOUR_MODEL_ARTIFACT_URI>" # TODO: Add the model artifact URI returned by the `union cache model-from-hf` command
MAX_MODEL_LEN = "71072"
WANDB_PROJECT = "phi-vllm"
WANDB_ENTITY = "<YOUR_WANDB_ENTITY>" # TODO: Add your wandb entity — this is your W&B username or team name
EMBEDDING_MODEL = "BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5"
llm_image = union.ImageSpec(
name="phi-vllm",
packages=["union[vllm]==0.1.182"],
builder="union",
apt_packages=["build-essential"],
)
vllm_app = VLLMApp(
name="phi-vllm",
container_image=llm_image,
requests=union.Resources(cpu=6, mem="20Gi", gpu="1", ephemeral_storage="200Gi"),
accelerator=GPUAccelerator("nvidia-l40s"),
model=MODEL_ARTIFACT_URI,
model_id=MODEL_ID,
scaledown_after=600,
stream_model=True,
extra_args=["--max-model-len", MAX_MODEL_LEN],
)stream_model streams the model directly from the artifact to the GPU,
avoiding disk I/O and significantly reducing load time during deployment.
scaledown_after controls cost by specifying how long (in seconds)
the model instance should remain active before scaling down when idle
Building and serving the RAG app
We start by defining the app’s container image, which includes all the necessary dependencies for the RAG pipeline.
app_image = union.ImageSpec(
name="weave-rag",
apt_packages=["ca-certificates"],
packages=[
"openai==1.74.0",
"llama-index==0.12.32",
"llama-index-vector-stores-weaviate==1.3.1",
"llama-index-embeddings-fastembed==0.3.1",
"llama-index-llms-openai-like==0.3.4",
"fastapi[standard]==0.115.12",
"weave[scorers]==0.51.43",
"union-runtime>=0.1.17",
"weaviate-client==4.14.3",
"spacy==3.8.5",
],
commands=["python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm"],
builder="union",
)We use FastAPI to handle incoming requests and define the API endpoints.
In the lifespan function, we initialize the app’s state with the LLM client, Weaviate client, and NLP model.
We also set up the relevancy and hallucination scorers to enable guardrails in the RAG app.
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app):
import spacy
import weave
import weaviate
from llama_index.llms.openai_like import OpenAILike
from weave.scorers import ContextRelevancyScorer, HallucinationFreeScorer
from weaviate.classes.init import AdditionalConfig, Auth, Timeout
# `WANDB_PROJECT` environment variable is set by `WeaveConfig`.
weave.init(project_name=os.getenv("WANDB_PROJECT"))
app.state.llm_client = OpenAILike(
model=MODEL_ID,
api_base=f"{os.getenv('VLLM_PHI_ENDPOINT')}/v1",
api_key="abc",
max_tokens=2048,
is_chat_model=True,
is_function_calling_model=True,
)
app.state.vdb_client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud(
cluster_url=os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL"),
auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY")),
additional_config=AdditionalConfig(timeout=Timeout(init=30)),
)
relevancy_prompt = """
Given the following question and context, rate the relevancy of the context to the question on a scale from 0 to 1.
Question: {question}
Context: {context}
Relevancy Score (0-1):
"""
app.state.hallucination_scorer = HallucinationFreeScorer()
app.state.relevancy_scorer = ContextRelevancyScorer(
relevancy_prompt=relevancy_prompt, column_map={"output": "query"}
)
app.state.nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
yield
# Cleanup
vdb_client.close()Filters are used to narrow down the search results, and in this case, we want to extract metadata from the user query to create filters for retrieving relevant listings.
We define an extract_filters_from_query function to convert the extracted metadata into a
structured Weaviate filter.
def extract_filters_from_query(query: str, nlp):
from weaviate.classes.data import GeoCoordinate
from weaviate.classes.query import Filter
filters = []
price_range = extract_price_range(query, nlp)
if price_range:
if "min_price" in price_range:
filters.append(
Filter.by_property("price").greater_or_equal(price_range["min_price"])
)
if "max_price" in price_range:
filters.append(
Filter.by_property("price").less_or_equal(price_range["max_price"])
)
number_of_reviews = extract_number_of_reviews(query, nlp)
if number_of_reviews:
filters.append(
Filter.by_property("number_of_reviews").greater_or_equal(number_of_reviews)
)
if re.search(r"\b(superhost|superhosts|only superhosts)\b", query, re.I):
filters.append(Filter.by_property("host_is_superhost").equal("t"))
if re.search(r"\b(instant book|instant bookable|instant booking)\b", query, re.I):
filters.append(Filter.by_property("instant_bookable").equal("t"))
if match := re.search(r"(?:rating|review score)[^\d]*(\d(?:\.\d)?)", query, re.I):
filters.append(
Filter.by_property("review_scores_rating").greater_or_equal(
float(match.group(1))
)
)
location_name = extract_location(query, nlp)
if location_name:
lat, lon = geocode_location(location_name)
if lat is not None and lon is not None:
filters.append(
Filter.by_property("location").within_geo_range(
coordinate=GeoCoordinate(latitude=lat, longitude=lon),
distance=10000, # in meters
)
)
print(f"Filters: {filters}")
return Filter.all_of(filters=filters) if filters else NoneLogging entire inputs and outputs to Weave isn’t always necessary or desirable, and so we define pre- and post-processing functions to selectively log inputs and outputs to Weave.
def postprocess_inputs(inputs: dict[str, typing.Any]) -> dict[str, typing.Any]:
return {k: v for k, v in inputs.items() if k != "request"}
def postprocess_output(outputs: dict) -> str:
return outputs["output"]Next, we define the generate_rag_response function with @weave.op to enable tracing.
This function processes user queries by generating filters, retrieving relevant listings from Weaviate,
and generating responses with the Phi-3 model. It also extracts source nodes from the response to
provide context — helpful for applying guardrails like relevancy and hallucination checks.
@weave.op(postprocess_inputs=postprocess_inputs, postprocess_output=postprocess_output)
async def generate_rag_response(query: str, request: Request) -> dict:
from llama_index.core import Settings, VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from llama_index.core.query_engine import RetrieverQueryEngine
from llama_index.embeddings.fastembed import FastEmbedEmbedding
from llama_index.vector_stores.weaviate import WeaviateVectorStore
Settings.embed_model = FastEmbedEmbedding(model_name=EMBEDDING_MODEL)
Settings.llm = request.app.state.llm_client
vector_store = WeaviateVectorStore(
weaviate_client=request.app.state.vdb_client, index_name=os.getenv("INDEX_NAME")
)
loaded_index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(vector_store)
filters = extract_filters_from_query(query, request.app.state.nlp)
retriever = loaded_index.as_retriever(vector_store_kwargs={"filters": filters})
SUMMARY_TEMPLATE = PromptTemplate(
"""You are a travel assistant helping someone find a place to stay.
Use the information below to answer the user's query clearly and helpfully.
Compare the listings and provide a concise summary of the most relevant ones.
Listings:
{context_str}
Suggested Answer:
"""
)
query_engine = RetrieverQueryEngine.from_args(
retriever, response_mode="tree_summarize", summary_template=SUMMARY_TEMPLATE
)
response = query_engine.query(query)
nodes = [
{
"text": node.get_content(),
"metadata": node.metadata,
}
for node in response.source_nodes
]
return {
"output": response.response,
"context": nodes,
}Finally, we define the FastAPI app along with the main application using Union’s App class.
The dependencies parameter ensures the LLM app is running before deploying the RAG app.
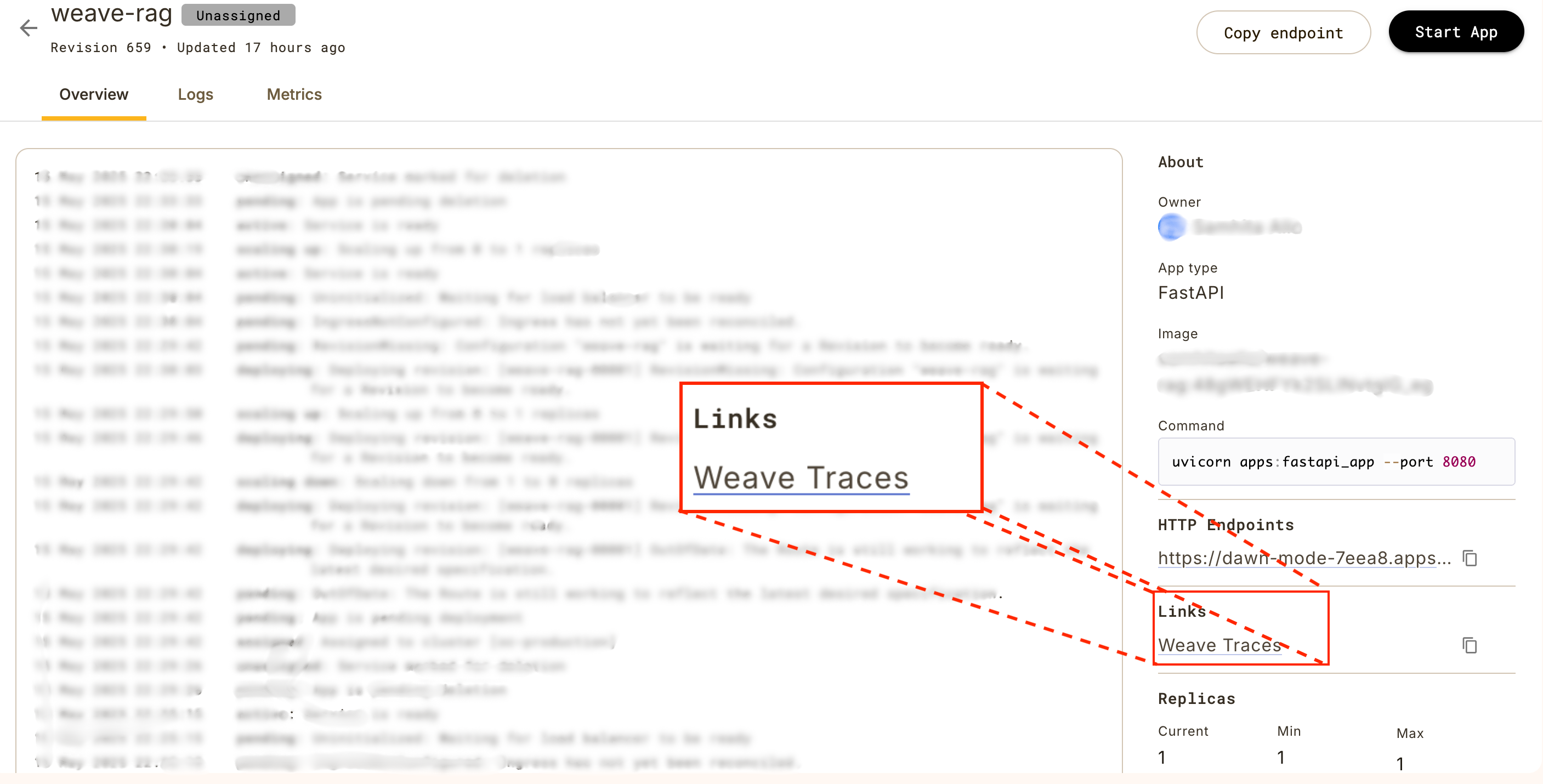
We use WeaveConfig to configure the Weave project and entity,
which generates a convenient link to the Weave dashboard.
This link is available on the app page for easy access to traces and insights.
fastapi_app = FastAPI(lifespan=lifespan)
app = App(
name="weave-rag",
secrets=[
union.Secret(key="wandb-api-key", env_var="WANDB_API_KEY"),
union.Secret(key="weaviate-url", env_var="WEAVIATE_URL"),
union.Secret(key="weaviate-api-key", env_var="WEAVIATE_API_KEY"),
# For scorers
union.Secret(key="openai-api-key", env_var="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
],
dependencies=[vllm_app],
framework_app=fastapi_app,
container_image=app_image,
inputs=[
Input(name="index_name", value="AirbnbListings", env_var="INDEX_NAME"),
Input(
name="VLLM_PHI_ENDPOINT",
value=vllm_app.query_endpoint(public=False),
env_var="VLLM_PHI_ENDPOINT",
),
],
config=WeaveConfig(entity=WANDB_ENTITY, project=WANDB_PROJECT),
limits=union.Resources(cpu="1", mem="5Gi"),
min_replicas=1,
)The app exposes a single endpoint, /query_rag, which accepts user queries.
Before returning a response, guardrails verify the model’s output to ensure accuracy and relevance.
We use built-in Weave scorers to detect hallucinations and assess relevancy.
You can also add custom scoring functions to validate the model’s output.
@fastapi_app.post("/query_rag")
@weave.op(postprocess_inputs=postprocess_inputs)
async def query_rag(query: str, request: Request) -> str:
result, call = await generate_rag_response.call(query, request)
# Guardrails
hallucination_response = await call.apply_scorer(
request.app.state.hallucination_scorer, {"context": result["context"]}
)
if hallucination_response.result["has_hallucination"]:
return f"The context contains hallucinations. Reasoning: {hallucination_response.result['reasonings']}"
relevancy_score = await call.apply_scorer(
request.app.state.relevancy_scorer, {"context": result["context"]}
)
relevancy_threshold = 0.6
if relevancy_score.result["relevancy_score"] < relevancy_threshold:
return f"The context is not relevant to the question. Reasoning: {relevancy_score.result['reasoning']}"
return result["output"]Example queries to test the app:
- “Find me a place in Amsterdam with a superhost and at least 100 reviews.”
- “Show me properties priced between $150 and $300 with a review score above 4.0.”
- “Find superhost listings with more than 50 reviews, rated over 4.5, and priced between $150 and $300.”
Utility functions
Below we define helper functions to parse Airbnb listings, extract relevant metadata, and identify filters mentioned in the user query.
We use the spacy library to extract entities like location and price range from the query.
def parse_listing_row(row: dict):
from llama_index.core import Document
from weaviate.classes.data import GeoCoordinate
metadata = {}
FIELDS = {
"price": float,
"review_scores_rating": float,
"number_of_reviews": int,
"host_is_superhost": str,
"instant_bookable": str,
}
for key, convert_fn in FIELDS.items():
raw_val = row.get(key, "").strip()
if raw_val:
try:
if convert_fn != str:
raw_val = (
raw_val.replace("$", "").strip() if key == "price" else raw_val
)
metadata[key] = convert_fn(raw_val)
else:
metadata[key] = raw_val
except ValueError as e:
print(f"[WARN] Failed to convert '{key}' value '{raw_val}': {e}")
continue
try:
latitude = float(row["latitude"])
longitude = float(row["longitude"])
metadata["location"] = GeoCoordinate(latitude=latitude, longitude=longitude)
except (KeyError, ValueError) as e:
print(f"[WARN] Invalid location data: {e}")
content = "\n".join(
f"{k.strip()}: {v.strip()}"
for k, v in row.items()
if k not in FIELDS and k not in ("latitude", "longitude")
)
return Document(text=content, metadata=metadata)
def extract_location(query, nlp):
doc = nlp(query)
for ent in doc.ents:
if ent.label_ in ("GPE", "LOC"):
return ent.text # Return first location found
return None # No location found
def geocode_location(location_name) -> tuple[float, float]:
import requests
url = "https://nominatim.openstreetmap.org/search"
params = {"q": location_name, "format": "json", "limit": 1}
headers = {"User-Agent": "llamaindex-weaviate-rag"}
response = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
results = response.json()
if results:
lat = float(results[0]["lat"])
lon = float(results[0]["lon"])
return lat, lon
else:
return None, None
def extract_price_range(query, nlp):
query_lower = query.lower()
doc = nlp(query)
money_values = [ent.text for ent in doc.ents if ent.label_ == "MONEY"]
# Extract numeric part from MONEY strings like "$200", "300 dollars"
numbers = []
for m in money_values:
match = re.search(r"\d+", m.replace(",", ""))
if match:
numbers.append(int(match.group()))
if "under" in query_lower or "below" in query_lower or "less than" in query_lower:
if numbers:
return {"max_price": numbers[0]}
if "over" in query_lower or "above" in query_lower or "more than" in query_lower:
if numbers:
return {"min_price": numbers[0]}
if "between" in query_lower or "from" in query_lower:
if len(numbers) >= 2:
return {"min_price": numbers[0], "max_price": numbers[1]}
if len(numbers) == 2 and re.search(r"\d+\s*(to|-|and)\s*\d+", query_lower):
return {"min_price": numbers[0], "max_price": numbers[1]}
if len(numbers) == 1:
# Fallback guess — likely a max price
return {"max_price": numbers[0]}
return None
def extract_number_of_reviews(query, nlp):
from spacy.matcher import Matcher
matcher = Matcher(nlp.vocab)
# Match phrases like "at least 50 reviews", "over 100 reviews", "100+ reviews"
matcher.add(
"REVIEW_COUNT",
[
[{"LIKE_NUM": True}, {"LOWER": {"IN": ["reviews", "review"]}}],
[
{"LOWER": {"IN": ["over", "more", "at", "least"]}},
{"LIKE_NUM": True},
{"LOWER": {"IN": ["reviews", "review"]}},
],
],
)
doc = nlp(query)
matches = matcher(doc)
for _, start, end in matches:
span = doc[start:end]
for token in span:
if token.like_num:
return int(token.text)
return None